Cosmic ray research in Yerevan Physics Institute (all the day)
|
|
 
|
|
In 1942, the physicists Abram and Artem Alikhanian started cosmic ray detection on Mount Aragats. They have found high-energy protons, deuterons and new unstable particles in the flux of cosmic rays. These initiated the regular study of cosmic rays. At present, the Aragats Space Environmental Center (Cosmic Ray Division) uses several detector systems at Aragats and Nor-Amberd stations on Mt Aragats, at lake Sevan and other places. In addition to cosmic rays, natural electron acceleration within the clouds above the Aragats are studied. A mechanism of particle acceleration and multiplication in thunderclouds was described. One of the most important accomplishments of the Cosmic Ray Division (CRD) was the launching of the Armenian Geophysical Network (AGN), which provides measuring and analyzing of environmental parameters for global change research and natural disaster forecasting.
|
| Isotopes research and their production |
|
 At present, radionuclides are used for the diagnosis and radiotherapy of tumor and non-tumor diseases. Radionuclides are most widely used in nuclear medicine, and in recent years also for assessing the state of the environment. For medical purposes nuclear reactors are used in the production of radionuclides, but this method is accompanied by a high yield of long-lived radionuclides. The use of accelerators significantly reduces the number of long-lived radionuclides. At present, radionuclides are used for the diagnosis and radiotherapy of tumor and non-tumor diseases. Radionuclides are most widely used in nuclear medicine, and in recent years also for assessing the state of the environment. For medical purposes nuclear reactors are used in the production of radionuclides, but this method is accompanied by a high yield of long-lived radionuclides. The use of accelerators significantly reduces the number of long-lived radionuclides.
For medical purposes, new accelerator methods are being developed that will make it possible to obtain the isotopes Gallium-67 (67Ga), Indium-111 (111In), Iodine-123 (123I), Thallium-201 (201Tl), Technetium-99m (99mTc), α-emitters 213Bi-DOTATOC, Actinium-225 (225Ac) and others (R. Avakyan, A. Avetisyan et al, 2009). We can find out about these modern methods and studies at the Isotopes Research and Production Department.
|
| Armenian NPP |
|
 The Armenian NPP was built in 1969-1977 near the city of Metsamor. NPP consists of two power units with VVER-440 reactors. In 1988, the power units were stopped due to the earthquake in the Spitak town. In 1993 and 1995 NPP operation has been restored. In 2017-2020, it is planned to modernize the NPP with a view to its radiation safety. The radioactive waste and spent nuclear fuel management system will also be modernized. Nuclear plant fallouts are controlled by the NPP service and the Center for Ecological and Noospheric Research (CENS NAS RA). Biophysicists of the Applied Physics Research Division (APRD) analyze the NPP effects on soil microbiota in the NPP 30-km zone (G. Khachatryan et al 2016). Control, diagnosis and treatment of patients with general and local radiation injuries are carried out in the Department of Radiation Injuries of the National Burn Center of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Armenia. A meeting is planned with employees of the NPP radiation safety department and the CENS. The Armenian NPP was built in 1969-1977 near the city of Metsamor. NPP consists of two power units with VVER-440 reactors. In 1988, the power units were stopped due to the earthquake in the Spitak town. In 1993 and 1995 NPP operation has been restored. In 2017-2020, it is planned to modernize the NPP with a view to its radiation safety. The radioactive waste and spent nuclear fuel management system will also be modernized. Nuclear plant fallouts are controlled by the NPP service and the Center for Ecological and Noospheric Research (CENS NAS RA). Biophysicists of the Applied Physics Research Division (APRD) analyze the NPP effects on soil microbiota in the NPP 30-km zone (G. Khachatryan et al 2016). Control, diagnosis and treatment of patients with general and local radiation injuries are carried out in the Department of Radiation Injuries of the National Burn Center of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Armenia. A meeting is planned with employees of the NPP radiation safety department and the CENS.
|
CANDLE – Center for the Advancement of Natural Discoveries using Light Emission
|
|
|
|
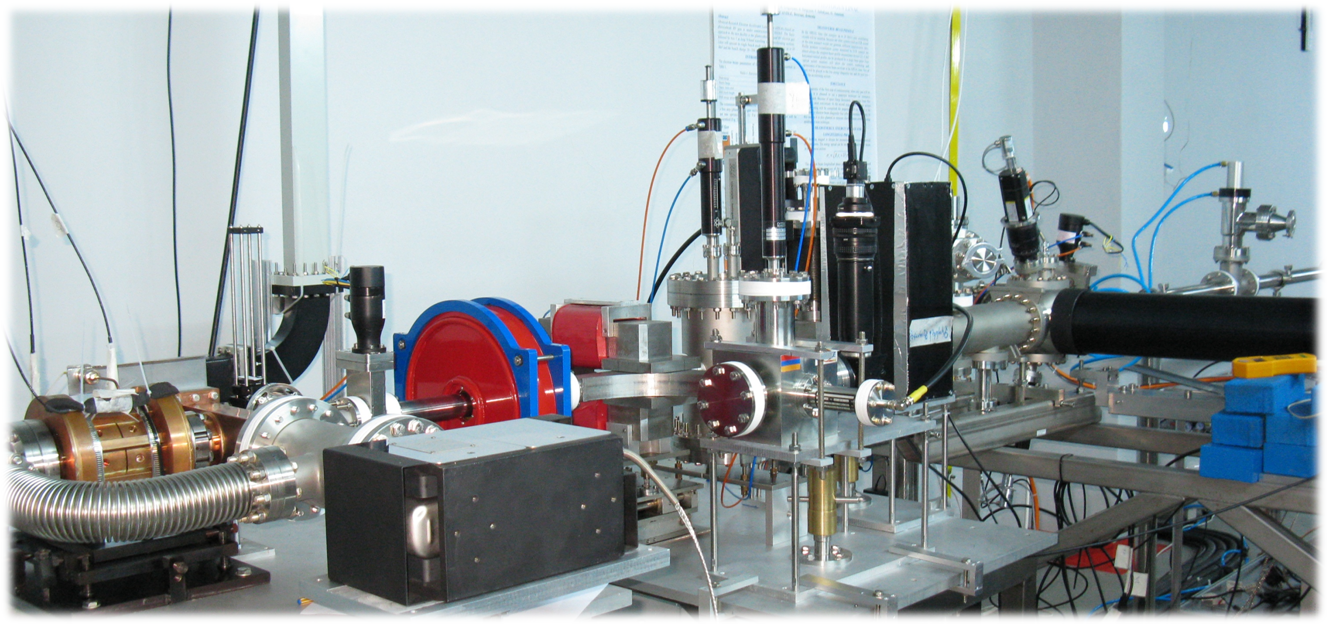
CANDLE - is a project of 3 GeV energy, third generation synchrotron light source for fundamental, industrial and applied research in biology, physics, chemistry, medicine, material and environmental sciences.
As a first phase of CANDLE project - AREAL (Advanced Research Electron Accelerator Laboratory) - is a 5 MeV laser driven electron accelerator, presently running at CANDLE institute successfully serving irradiation experiments in fields as: life and material sciences, medicine, pharmacy, new accelerator technologies, etc.
Satellite laboratories of: Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Two-photon microscopy, laser technologies and optics, vacuum technology are accomplishing instrumental abilities for research and study of radiation effects at CANDLE Institute.
The formation of a strong user community and annual organization of international practical courses for students are the keys of success for scientific-technological developments.
|



 At present, radionuclides are used for the diagnosis and radiotherapy of tumor and non-tumor diseases. Radionuclides are most widely used in nuclear medicine, and in recent years also for assessing the state of the environment. For medical purposes nuclear reactors are used in the production of radionuclides, but this method is accompanied by a high yield of long-lived radionuclides. The use of accelerators significantly reduces the number of long-lived radionuclides.
At present, radionuclides are used for the diagnosis and radiotherapy of tumor and non-tumor diseases. Radionuclides are most widely used in nuclear medicine, and in recent years also for assessing the state of the environment. For medical purposes nuclear reactors are used in the production of radionuclides, but this method is accompanied by a high yield of long-lived radionuclides. The use of accelerators significantly reduces the number of long-lived radionuclides. The
The 


